SEO isn’t constant; it’s changing its ranking factors rapidly. That’s why keeping up your strategy with Google’s updates is a must. With new algorithms and search trends popping up, some terms have become essential to understand and keep in the know.
Falling behind on these updates could mean losing out on valuable rankings and missing chances to connect with your audience.
In this article, I will discuss 25 new SEO terms you need to know to keep your SEO strategy updated in 2025.
25 New SEO Terms You Should Know in 2025
Here are those new terms and practices you should follow to stay ahead of your competitors. The faster you adopt the better your rankings will grow.
1. AI Overview in SEO
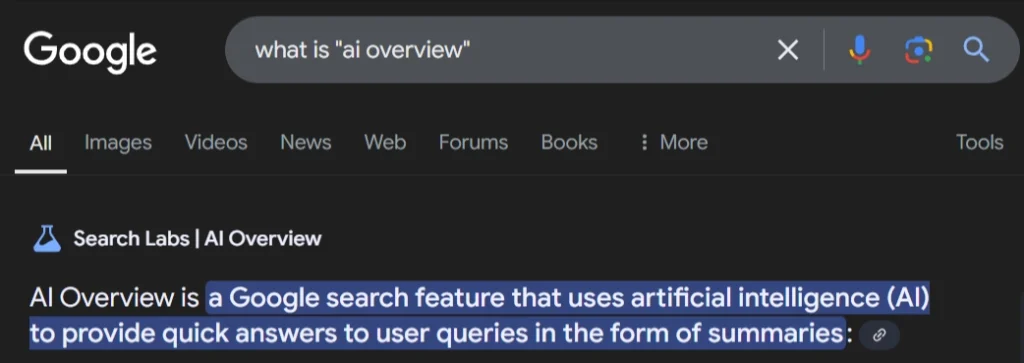
AI Overview is a summary or snippet generated by Artificial Intelligence that provide concise, relevant, and context-aware information directly on a search engine results page (SERP).
AI-driven technologies, like Google’s MUM (Multitask Unified Model) and RankBrain, analyze content on a deeper semantic level, focusing on the relationships between entities and topics rather than just matching keywords.
How AI Overview Works:
-AI analyzes large datasets to understand how users phrase their queries and the intent behind them.
-It improves search results by connecting seemingly unrelated topics or questions based on the relationships in content (semantic understanding).
-AI helps generate features like Knowledge Panels, Featured Snippets, and AI Overviews, providing users with direct answers and context-rich information.
For SEOs, Adopting AI Overview Practices Means Creating Content That:
– Aligns with semantic search principles by targeting entities and their context.
– Focuses on user experience by delivering detailed, authoritative, and comprehensive answers.
– Incorporates structured data and schema to help AI better understand the content.
– By embracing this trend, you can improve your content’s visibility in AI-driven search results, ensuring it ranks well and meets user expectations in 2025.
2. Search Generated Experience (SGE)
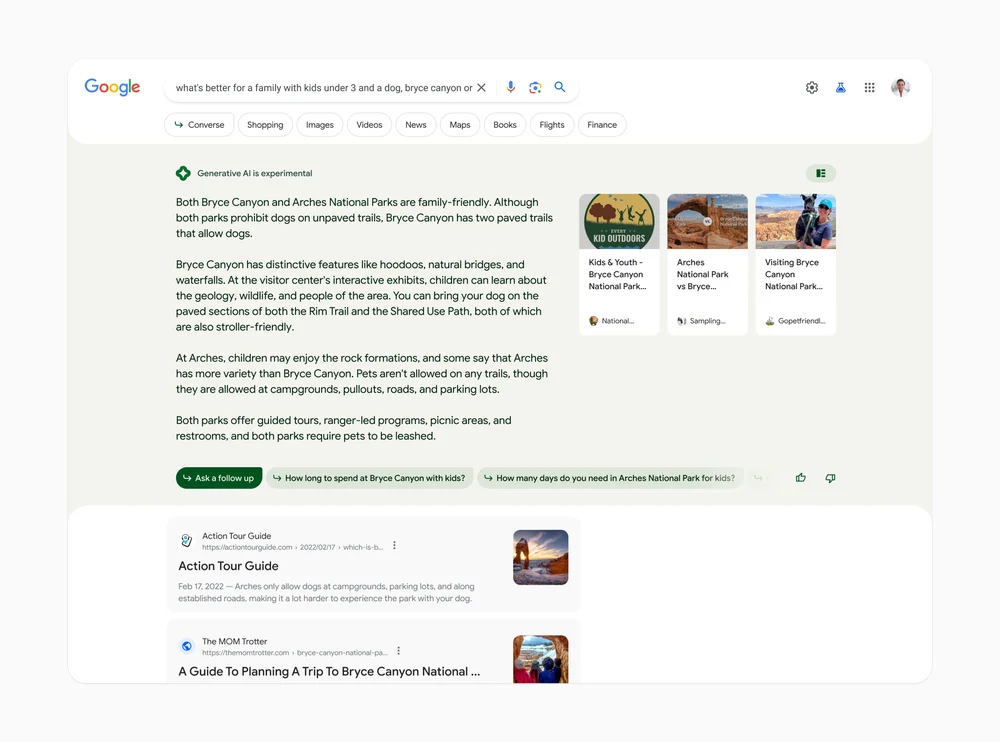
Image Source
Search Generated Experience (SGE) is a way that search engines, like Google, improve how users find information by using AI-created content and personalized insights right in the search results. Instead of just showing a list of links, SGE gives users quick, relevant answers, recommendations, or summaries based on what they’re looking for.
How SGE Works:
SGE is driven by new developments in AI, especially generative AI and large language models (LLMs). When someone searches for something, the AI understands what they mean and creates responses that mix existing information (like webpages and databases) with easy-to-understand summaries. These results usually include:
- Direct Answers: AI-generated explanations or summaries that directly answer the question.
- Interactive Features: Suggestions, follow-up questions, or expandable sections for further exploration.
- Personalized Content: Insights based on the user’s search history, preferences, or location.
For example, if you search for “Best cameras for photography beginners,” SGE might:
- Show a list of top camera models along with their advantages and disadvantages.
- Highlight important reviews or user feedback.
- Offer interactive questions like, “Do you prefer DSLR or mirrorless cameras?”
Why SGE Important for SEO:
- Content Optimization: Businesses need to make sure their content is clear and organized to match what users are looking for so they can appear in SGE results.
- Entity Optimization: Since SGE uses Knowledge Graphs and semantic entities, focusing on entity-based SEO is essential.
- User Engagement: By showing up in these enhanced search experiences, brands can gain more visibility and attract more engagement compared to regular search results.
One of the biggest trends is customized SEO packages for 2025 that suit different industries and budgets.
Differences Between AI Overview & SGE :
Although Google SGE and AI Overviews are often used as if they mean the same thing, they are actually different. Google SGE is a version created by Google Labs that has features not found in AI Overviews.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Search Generated Experience (SGE) | AI Overview |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improve the entire search journey with context and interactivity | Provide concise, high-level answers |
| Scope | Wider in scope, addressing various and detailed questions. | Narrow, focused on quick queries |
| Interactivity | Offers dynamic elements, follow-up questions, and options to explore deeper | Typically static, offering a single answer or summary |
| Technology | Powered by generative AI and LLMs to create summaries from multiple sources | Uses AI to extract and condense information |
| Placement in Search | Often spans multiple sections of the search results | Displayed at the top as a snippet or summary |
3. Entity-First Indexing
The way we approach content and search engine rankings is changing, driven by two contrasting strategies: Entity-First and Keyword-First. For a long time, traditional SEO focused mainly on keywords to determine relevance. However, with the rise of semantic search, the focus is shifting toward an Entity-First approach.
What is Entity-First Indexing ?
An Entity-First strategy focuses on semantic SEO (optimizing for meaning and context) by prioritizing entities—such as concepts, people, or organizations—over traditional keyword-focused approaches. This approach focuses on understanding the relationships and context surrounding entities, which are usually found in Knowledge Graphs and Knowledge Panels.
By targeting entities, content becomes more aligned with how Google interprets user intent, going beyond specific keywords to deliver more relevant and meaningful search results.
Applying an Entity-First Strategy in Practice
Imagine you’re creating content about “Machine Learning.”
Traditional Keyword-Focused Approach:
A keyword-focused strategy would involve targeting phrases like:
-What is machine learning?
-Best machine learning tools
-Machine learning examples
The content might repeat these keywords frequently and focus solely on ranking for them, without focusing the deeper meaning or connections of the topic.
Entity-First Approach:
With an Entity-First strategy, the focus shifts to “Machine Learning” as an entity.
Here’s how it works:
-Machine Learning is an entity connected to other concepts, such as Artificial Intelligence, algorithms, data analysis, and neural networks.
-These connections are part of Google’s Knowledge Graph.
- -Instead of stuffing keywords, you would create content that explains Machine Learning’s context, such as:
- How it relates to Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Its use cases across industries like healthcare and finance.
- Tools and algorithms commonly used in Machine Learning.
-Mention related entities that appear in Knowledge Graphs, such as “Supervised Learning,” “Deep Learning,” and “Natural Language Processing.”
-Include people (e.g., Alan Turing), organizations (e.g., OpenAI), and concepts (e.g., Neural Networks) tied to Machine Learning.
-Address questions Google is likely trying to answer based on user intent, such as:
- What is the role of Machine Learning in AI?
- How do Machine Learning algorithms work?
- What industries benefit the most from Machine Learning?
Why Entity-First SEO Aligns Better with Semantic Search
Semantic search depends on two main elements that Entity-First strategies handle really well:
Context and Intent Recognition: By focusing on specific entities, Google can see how different concepts are connected, which helps it respond better to more complex search questions. This means it can understand synonyms, abbreviations, and related terms, leading to more accurate results instead of just matching keywords.
Content Organization with Topical Maps: Entity-First SEO often includes creating a topical map, which is a way to organize content that makes sure all important aspects of a subject are addressed, from main topics to related subtopics. This method shows expertise by thoroughly covering a topic, aligning the content with what users are looking for, and enhancing the accuracy of the results.
4. Hybrid Intent Modeling

Image Source
Hybrid Intent Modeling is a modern method used to understand and predict what users are looking for when they search online. It combines different sources of information and uses AI technology.
Unlike older methods that just sort search queries into basic groups, like informational, transactional, or navigational, hybrid intent modeling looks at user behavior, the context of the search, and real-time signals.
This approach provides a deeper and more flexible understanding of what users really want.
How Hybrid Intent Modeling Works:
Hybrid intent modeling utilizes structured data (like query types, demographics, or user profiles) alongside unstructured data (e.g., recent browsing history, clicked links, or device usage patterns) to infer intent with greater accuracy.
Then AI models process this data to identify patterns and predict intent across various contexts. For example, a user searching for “best laptops” could be shown personalized results depending on their previous searches (e.g., “budget-friendly” or “gaming laptops”).
5. Hyperlocal Targeting
Hyperlocal targeting is a specific approach to location-based SEO that aims to connect with users in a very small geographical area, like a neighborhood, block, or even a single building. This strategy is especially helpful for businesses such as coffee shops, restaurants, gyms, and local service providers that depend on nearby customers.
How Hyperlocal Targeting Works:
- Geo-Specific Keywords: Use very specific keywords in your content, like “coffee shop near [landmark]” or “plumber in [neighborhood name].”
- Google Business Profile Optimization: Make sure your Google Business Profile (GBP) profile is complete with accurate information, including your address, phone number, and hours of operation. Use Google Posts to share local events or special offers.
- Localized Content: Create content that is relevant to your area. For example, writing a blog post titled “Top 5 Outdoor Activities in [Neighborhood]” can help attract more visitors and keep your content relevant.
- Micro-Moment Marketing: Use targeted ads that reach people searching for services “near me” or those who are physically located close to your business.
- Proximity Signals: Make sure your business is listed accurately on local directories and apps like Yelp or TripAdvisor to help search engines recognize your location better.
6. Sentiment-Driven SEO

Sentiment-Driven SEO is a modern optimization technique that focuses on understanding user sentiment (positive, neutral, or negative) to shape content strategies and improve rankings. It goes beyond traditional keyword-focused approaches by understanding how users feel about a topic, brand, or product.
How Sentiment-Driven SEO Works:
Businesses use advanced AI tools to look at user feedback, reviews, social media comments, and other content to determine the overall sentiment of these conversations. These tools can categorize the text as positive, neutral, or negative.
Once they know the main sentiment, marketers create content that boosts positive feelings, addresses negative feedback, or presents balanced and informative views on neutral topics.
7. EEAT-Driven Structured Data
EEAT stands for Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trustworthiness, a core concept in Google’s evaluation of high-quality content. EEAT-driven structured data refers to the implementation of schema markup designed to showcase these attributes on your website to search engines.
How it Works:
Structured data, like schema.org markup, provides search engines with detailed information about your website and its content. To leverage EEAT principles, you can use structured data to highlight critical elements that demonstrate your expertise, authority, and trustworthiness. Here’s how it can be applied:
Expertise(E):
Use Person schema to link expert contributors, showcasing their credentials and professional roles.
Example: If a healthcare blog is written by a doctor, include their medical credentials in the schema.
Experience (E):
Showcase real-world experience through Review schema or FAQ schema that highlights testimonials, case studies, or hands-on insights.
Example: A product page with detailed customer reviews or user-generated insights.
Authority (A):
Use Organization schema to display awards, affiliations, or certifications that add credibility to your brand.
Example: Highlight your company’s partnerships or industry recognition
Trustworthiness (T):
Include Breadcrumb schema and SiteNavigation schema to improve transparency and make your website easy to navigate.
Example: Secure transactional pages (e.g., e-commerce checkout) with HTTPS structured data.
8. Engagement Metrics Priority
In 2025, search engines like Google are paying more attention to engagement metrics to decide how good and relevant content is. Engagement metrics include things like click-through rates (CTR), how long people stay on a page (dwell time), bounce rate, and how far down they scroll. These metrics are important because they show how users interact with a webpage after clicking on it.
Here’s how Engagement Metrics Priority Works:
When someone searches for something and clicks on a link, search engines keep track of what they do. If the user spends a lot of time on the page, scrolls through the content, or interacts with things like videos, images, or links, it indicates that the content is interesting and helpful.
On the other hand, if the user quickly leaves the page (which is called a high bounce rate), it suggests that the content might not be relevant or useful to them.
9. Contextual Sentiment
Contextual Sentiment is an advanced way of understanding how people feel about content. It looks at not only whether the feelings are positive, negative, or neutral, but also the situation in which those feelings are shown.
This concept merges advanced natural language processing (NLP) with behavioral insights to evaluate the emotional tone in relation to specific topics, intent, and user expectations.
How Contextual Sentiment Works:
Search engines are increasingly using AI to determine if content matches what users are looking for, both emotionally and contextually. For example, if someone searches for “best winter jackets,” content that has a positive and enthusiastic tone about specific jackets might rank higher than plain, factual descriptions.
How to Optimize for It:
- Use Sentiment Analysis Tools: Use tools that can help you understand the emotional tone of your content to make sure it matches what users want.
- Create User-Focused Content: Think about what users are feeling when they make their search. If they are looking for solutions, show empathy for their problems. If they are ready to buy, use persuasive and positive language.
- Monitor and Adapt Reviews: Make sure that the reviews and testimonials on your site reflect the right feelings for your audience.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Write in a way that feels real, engaging, and emotionally connected to both users and search engines.
- Semantic Relevance: Combine emotionally appealing content with keywords that align with user intent to support positive feelings.
10. Behavior-Based Indexing
Behavior-Based Indexing is a modern idea in search engine optimization (SEO) that ranks web pages based on how users behave and interact with the content, instead of just looking at fixed things like keywords and backlinks. This method fits well with the increasing importance of user experience (UX) in how search engines decide which pages to show.
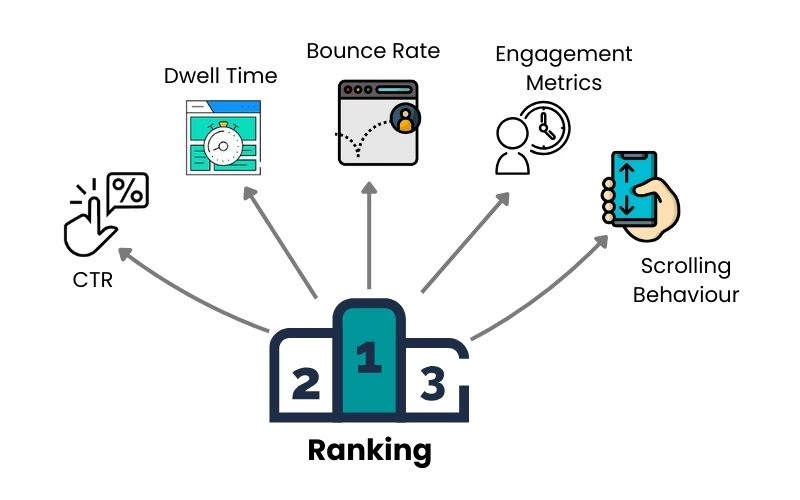
This includes tracking metrics like:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): How often users click on a link when it appears in search results.
- Dwell Time: The length of time users spend on a webpage after clicking on it from the search engine results page (SERP).
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of users who leave a webpage without interacting further.
- Scrolling Behavior: How much of the page users scroll through.
- Engagement Metrics: Activities like commenting, sharing, or clicking on embedded links.
How Behavior-Based Indexing Works:
Here’s how the process typically works:
Data Collection: Search engines gather behavioral data through browser analytics, search patterns, and direct feedback mechanisms.
Analysis: Machine learning algorithms evaluate which pages provide the most engaging and satisfying experiences for specific queries.
Dynamic Ranking Adjustments: Based on this analysis, rankings are adjusted to favor pages that demonstrate higher user engagement and satisfaction.
Feedback Loop: The system constantly learns and changes rankings according to how user behavior changes over time.
For example, if users searching for “best smartphones 2025” frequently click on a particular page, spend several minutes reading, and explore related links, that page is likely to rank higher for that query over time.
11. Content Velocity
Content velocity refers to the speed and frequency at which a brand or website publishes new content. It’s not just about volume; it’s about maintaining a consistent pace of content creation that aligns with audience demand, industry trends, and algorithm preferences.
In 2025, content velocity has become a crucial SEO factor because search engines prioritize fresh and relevant content to meet user expectations. Google’s algorithms, for example, are increasingly adept at recognizing websites that continuously provide valuable, up-to-date information.
12. Trend-Responsive Content
Trend-responsive content is a modern strategy in SEO that focuses on matching your content with the latest trends and current events. This means quickly spotting popular topics, changes in your industry, or important moments in society and creating high-quality, relevant content about them before your competitors do.
To use this strategy effectively, brands need to keep an eye on news sources, social media, and tools that predict trends. Using AI tools for content ideas can also help find trending keywords and topics that people are searching for a lot.
The main points are speed and relevance—publishing content that connects with what people are interested in right now can lead to more engagement, better rankings on search engines, and more shares on social media.
13. Semantic Similarity Clusters
Semantic Similarity Clusters are about putting together different pieces of content that are similar in meaning and context. This approach helps create a more organized content strategy that focuses on what users really want.
Unlike the old way of grouping content by individual keywords, semantic similarity clusters group topics based on how they’re related in meaning and importance. The main goal is to better understand how users think and what they search for.
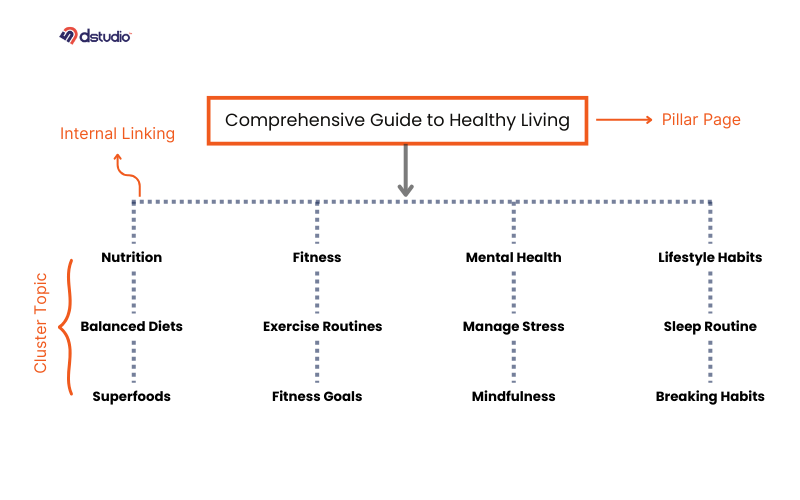
How to Create Semantic Similarity Clusters:
- Do Topic Research: Use tools like natural language processing (NLP) models or AI platforms to find out how different topics and subtopics are connected. Pay attention to what users are searching for, their intentions, and their overlapping interests.
- Make Pillar Pages: Create detailed pillar pages that act as the main source for a specific semantic cluster. These pages should cover broad topics and link to more detailed content that supports them.
- Write Supporting Content: Produce in-depth articles, blog posts, or guides that dive into subtopics related to your main pillar content. Make sure they connect to the central theme of the cluster.
- Optimize Internal Links: Link related content together to form a network of resources within the same cluster. This helps search engines understand how your content is related and improves your authority on the topic.
- Use Semantic Keywords: Instead of just focusing on single keywords, include related terms and phrases naturally in your writing.
14. Dwell Time Optimization
Dwell time refers to the amount of time a user spends on a webpage after clicking on a search engine result before returning to the search results. In SEO, it’s a critical user experience signal that search engines like Google may consider when determining the relevance and quality of a page.

Image Source
How to Optimize for Dwell Time:
- Create High-Quality, Engaging Content
- Optimize Page Load Speed
- Focus on Intent Matching
- Implement Interactive Elements like quizzes , calculators, polls.
- Ensure Mobile-Friendly Design
- Improve Internal Linking
- Use Video Content
15. Cumulative Intent Shifts
Cumulative Intent Shifts is a term that describes how a person’s intentions change as they go through their search process. User intent is not fixed; it changes and develops as people interact with search engines, look through results, and narrow down their searches.
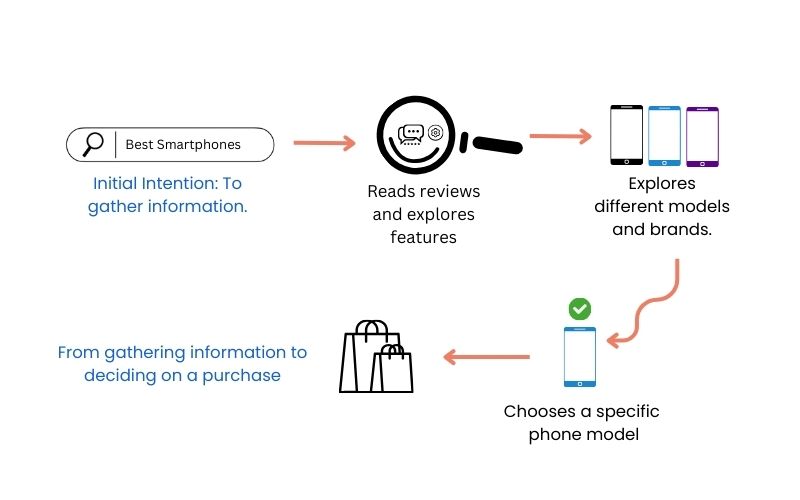
For example, a user searching for “best smartphones” may initially intend to gather information. But as they click on links, read reviews, and explore different features, their intention can shift towards specific phone models, brands, or even deciding to make a purchase. These changes in intention are what we call cumulative shifts.
How to Optimize for Cumulative Intent Shifts:
Examine the common steps users take when searching for important topics in your field.
Divide the process into four stages: awareness, consideration, decision, and post-purchase.
Make sure to create content that addresses each stage to keep it helpful and relevant during their search.
16. Implicit Intent Recognition
Implicit Intent Recognition is when search engines figure out what users really mean when they type something in, even if they don’t say it directly. For example, if someone types “best laptops,” the search engine can guess if they’re looking for reviews, buying tips, or affordable options, even if they don’t specify.
To do this, search engines look at things like where the user is, what type of device they’re using, their browsing history, and even the time of day. This helps them give more personalized search results.
Because of this, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) strategies need to focus on creating content that has a lot of context and can meet different user needs. Marketers should aim to produce detailed and well-organized content that addresses both what users say they want and what they might be looking for without saying it outright.
17. NLP-Driven Summaries
NLP-Driven Summaries are short, automated pieces of content created by Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms. These summaries highlight the main points of a page or article while keeping the context clear and relevant. Search engines are starting to favor content that includes NLP-driven summaries because they provide users with quick, straightforward answers or insights.
How to Use NLP-Driven Summaries for Better SEO:
- Use NLP tools to create summaries for your articles and place them at the start or end of your content. Tools like OpenAI’s GPT models or other specialized NLP programs can be very helpful.
- Clear and organized summaries make it more likely that your content will show up in Google’s featured snippets, which can lead to more clicks.
18. Interactive Metric Prioritization
Interactive Metric Prioritization (IMP) is a new SEO method that focuses on how users interact with different parts of a webpage to improve content for higher search rankings and better user experiences.
Instead of looking at traditional metrics like bounce rates or how long people stay on a page, IMP focuses on specific interactions, like clicking buttons, using sliders, watching videos, or exploring expandable menus and interactive infographics.
Key Elements of IMP
- Micro-Engagements: These are small actions that users take, such as clicking on expandable FAQ sections, watching embedded videos, or liking and sharing content on the page.
- Scroll Depth Analysis: This measures how far down a page users scroll.
- Dynamic Heatmaps: These tools show where users click or hover on a page, helping to improve content placement and optimize Calls-to-Action (CTAs).
- Time Spent on Interactive Features: This tracks how long users engage with interactive elements like quizzes, polls, or calculators.
19. On-Scroll Engagement Tracking

It tracks how users engage with a webpage as they scroll through its content, giving valuable information about their real-time involvement.
This method looks at things like how far down the page users scroll, how fast they scroll, where they pause on certain sections, and how they interact with elements like images, videos, or pop-ups.
20. Authority-Weighted Internal Links
Authority-Weighted Internal Links are a smart SEO strategy that uses the popularity of your best-performing pages to help improve the rankings of other pages on your website.
Instead of treating all internal links the same, this method focuses on linking from pages that have strong authority—like those with a lot of visitors, good backlinks, or high user engagement—to pages that need a better ranking.
21. Video View Depth Ranking
Video View Depth Ranking is a new measure that search engines are starting to prioritize. It looks at how much of a video people watch before they leave. It’s no longer just about getting clicks or views; now, search engines care more about how engaged viewers are.
If people watch a large part of a video, it tells the search algorithm that the content is really interesting and important, which helps it rank higher in search results.
22. Mobile Gesture Tracking
Mobile Gesture Tracking is the study of how people use their fingers to interact with mobile devices, like swiping, pinching, tapping, and scrolling. As more people use their phones for searching the web, search engines are focusing on how users experience these mobile interactions.
By analyzing gesture tracking, businesses and marketers can learn how users move around their websites and find problems that might make it hard for people to engage.
For instance, if users are swiping too much or zooming in accidentally, it could show that there are issues with the website’s design or where the content is placed.
23. Attention SEO
Attention SEO is a new trend in digital marketing that highlights the importance of capturing user attention as a key factor for ranking. Attention SEO focuses on making content that keeps the audience engaged for longer periods.
This method matches up with the latest developments in AI algorithms and search engines, which are beginning to look at user engagement metrics like how long someone stays on a page, how far they scroll, and how often they interact with the content.
Tips for Using Attention SEO:
- Focus on creating mobile-friendly designs for users who are on the move.
- Write catchy headlines and subheadings to help readers easily follow your content.
- Use emotional language that connects with what your audience cares about or dreams of.
- Test your content and use tools like heatmaps and user analytics to find out where people lose interest, and make improvements to keep them engaged.
24. Multilingual Understanding
Search engines like Google and Bing have advanced their language models to better understand and process content in multiple languages within a single query. This means search engines can interpret queries mixing languages (e.g., “best comida italiana near me”) and deliver more accurate results.
How to Optimize for Multilingual Understanding
Create Multilingual Content: Optimize your website for different languages and regions with localized keywords, cultural nuances, and relevant images.
Implement Hreflang Tags: Use these to inform search engines about language-specific pages.
Focus on Translation Quality: Instead of direct translation, focus on culturally relevant localization.
Multilingual Keyword Research: Understand how people search in different languages, as search behaviors and terms can vary significantly.
25. AI Content Moderation
AI Content Moderation refers to the automated process of monitoring and evaluating user-generated content using artificial intelligence. This includes identifying harmful, spammy, or irrelevant content and makes sure they follow community rules.
By using AI, websites can maintain high-quality content standards, improve user experience, and reduce manual workload. For SEO, AI content moderation ensures that your site remains compliant with Google’s guidelines, avoiding penalties for low-quality or inappropriate content.






